The Parason Headbox is a cutting-edge innovation designed to elevate the papermaking process through its advanced features and precise control mechanisms. This state-of-the-art technology is engineered to optimize paper quality, enhance production efficiency, and ensure superior performance in papermaking operations. In this blog let’s know the working principle of headbox.
At the heart of the Parason Headbox is its sophisticated technology and robust construction. With an excellent jet quality and precise control over gsm profile Parason Headbox helps maintaining consistent paper quality. Its C-clamp design and stainless-steel construction offer durability and uniform nozzle geometry, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
Let’s delve into the key components and working principle of the headbox that make the Parason Headbox a game-changer in the industry.
Key Components and Their Functions
1. Functional Body Diagram: The headbox is composed of several essential parts:
· HC Header and LC Header: These headers manage high and low pulp flow, pressure and dilution.
· Dilution Control Valve: The dilution control valve particularly designed in Parason Hydraulic Headbox. It regulates the pulp flow and consistency, preventing floc formation.
· Mixing Chamber and Distribution Tubes: Ensure even distribution and mixing of pulp.
· Stilling Chamber and Turbulence Generator: Optimize laminar flow and pressure for smooth paper formation.
· Top Lip Beam, Slice Blade, and Bottom Lip Beam: Crucial for controlling the pulp flow over the wire section.
2. Dilution Control System: Provided in Parason Hydraulic Headbox, this advanced system maintains optimal pulp flow and consistency, ensuring smooth paper formation by effectively managing the feeding unit.
3. Pulsation Dampening Tank: Essential for maintaining a steady flow of pulp, this tank absorbs and reduces pressure fluctuations, ensuring consistent paper quality.
4. Stilling Chamber: Meticulous engineering in the transition from the distribution chamber to the stilling chamber optimizes flow and pressure, enhancing paper formation.
5. Lip Opening and Projection: The electrically adjustable lip allows for ideal conditions for pulp flow and distribution, significantly influencing paper quality.
6. Edge Control Technology: This technology ensures precise fiber orientation and prevents uneven edges, reducing losses and enhancing performance.
7. Slice Micro-Adjustment: Allows fine-tuning of the slice opening and impingement point during operation, ensuring optimal paper quality.
8. Dilution Control Valve: Parason Hydraulic Headbox with dilution control valve operates on the principle of “two tube bundles” with a stilling chamber, ensuring stable sheet formation and a broad operation window. The turbulence generator further enhances paper quality by promoting smooth flow transition and optimal deflocculation.
Types of Headbox
The two main types of headbox that Parason Machinery manufacture and supplies are
The working principle of headbox despite of its type is almost similar. Let’s see about the working principle of headbox step by step.
Working Principle of Headbox
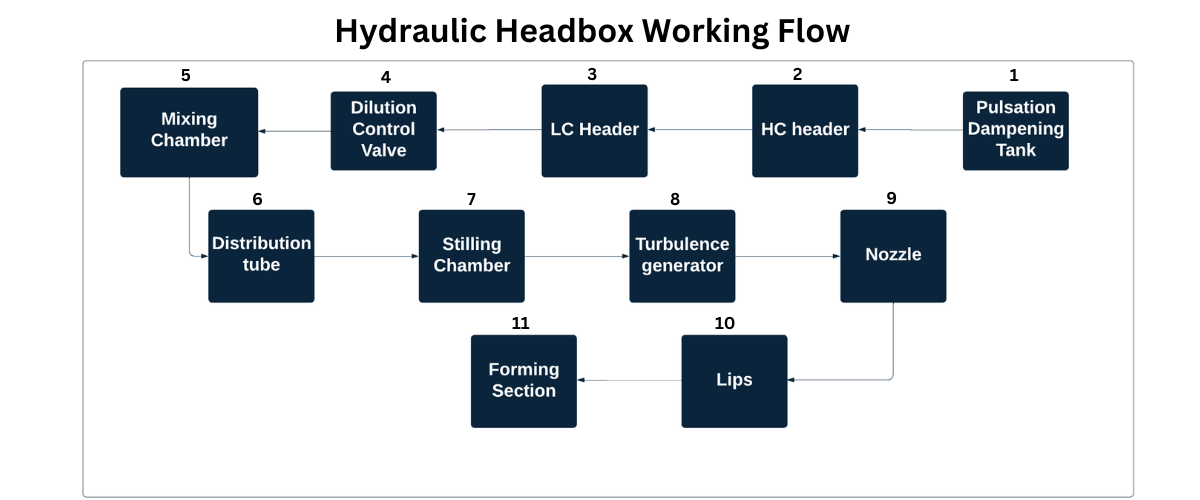
The headbox is a critical component in the papermaking process, responsible for delivering a uniform slurry of fiber and water onto the wire section of the paper machine. The working principle of a headbox, following the flow from the Pulsation Dampening Tank to the Wire Section, can be described as follows:
1. Pulsation Dampening Tank: The fiber suspension (pulp) enters the Pulsation Dampening Tank, which is designed to reduce pressure fluctuations and pulsations in the flow. This ensures a more stable and consistent flow of pulp to the subsequent stages.
2. HC Header: From the dampening tank, the pulp flows into the HC Header. This header distributes the pulp evenly across the width of the headbox. The HC header handles flow of pulp, which is then diluted in the following stages.
3. LC Header: The LC Header works for controlling consistency of the pulp.
4. Dilution Control Valve: The dilution control valve are designed in hydraulic headbox. The pressurized headbox does not contain the dilution control valve. This valve regulates the amount of water added to the pulp to control its consistency. It ensures precise dilution, enabling fine control over the fiber concentration before it reaches the wire section.
5. Mixing Chamber: In the Mixing Chamber, the diluted pulp is thoroughly mixed to ensure uniform consistency and distribution of fibers. This mixing is crucial for maintaining paper quality and uniformity.
6. Distribution Tube: The mixed pulp then flows through the Distribution Tube, which helps to distribute the slurry evenly across the width of the headbox. This tube ensures that the flow is uniform before it enters the next stage.
7. Stilling Chamber: The Stilling Chamber helps to calm the flow of pulp, reducing turbulence and ensuring a smooth, even flow. It acts as a settling area where any remaining inconsistencies in the flow are minimized.
8. Turbulence Generator: Despite the stilling chamber’s purpose, a certain amount of turbulence is reintroduced deliberately through the Turbulence Generator. This controlled turbulence helps to keep the fibers uniformly suspended in the water, preventing flocculation (clumping) and ensuring a uniform sheet formation.
9. Nozzle: The pulp slurry exits the headbox through the Nozzle, which is a narrow opening that directs the flow onto the wire. The design of the nozzle is crucial for ensuring that the slurry is evenly spread across the wire.
10. Lips: The headbox has adjustable lips (top and bottom) at the nozzle that control the thickness and velocity of the pulp slurry as it is discharged. These adjustments help to fine-tune the distribution and evenness of the slurry layer on the wire.
11. Forming Section: Finally, the pulp slurry is deposited onto the Wire Section, which is a moving mesh belt. Here, the water begins to drain away through the mesh, and the fibers start to form a continuous sheet of paper. The uniformity and consistency of the fiber distribution at this stage are crucial for the quality of the final paper product.
In summary, the headbox functions to convert a pulp slurry into a uniformly distributed, thin layer of fibers on the wire section, ensuring consistent paper quality. Each component in the flow sequence plays a specific role in managing the pulp’s consistency, distribution, and flow characteristics.
Parason Machinery is the premium name in the paper machinery manufacturing and supplying. For more details and detailed knowledge about the headbox and other paper machinery for your requirement you can contact us and get your answers as well as your solutions for your projects.